- Home
- The Vape Mall Blog
- Could CBD Help with Different Arthritis Conditions?
Could CBD Help with Different Arthritis Conditions?
Posted by on
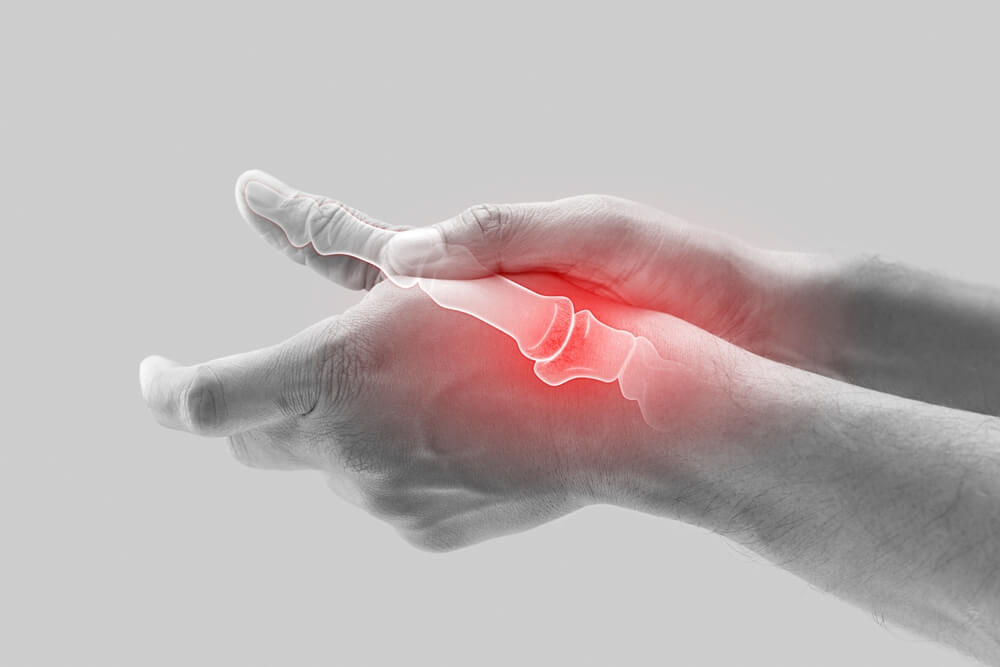 Arthritis,
a prevalent and often debilitating condition, affects millions of people
worldwide. Characterized by inflammation, pain, and stiffness
in the joints, arthritis can significantly impair quality of life. Traditional
treatments include medications, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery, but
these methods can have limitations and side effects. In recent years,
Cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychoactive compound derived from the cannabis plant,
has emerged as a potential alternative treatment for arthritis. This blog
explores the potential benefits, mechanisms, and research surrounding the use of
CBD in managing various forms of arthritis.
Arthritis,
a prevalent and often debilitating condition, affects millions of people
worldwide. Characterized by inflammation, pain, and stiffness
in the joints, arthritis can significantly impair quality of life. Traditional
treatments include medications, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery, but
these methods can have limitations and side effects. In recent years,
Cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychoactive compound derived from the cannabis plant,
has emerged as a potential alternative treatment for arthritis. This blog
explores the potential benefits, mechanisms, and research surrounding the use of
CBD in managing various forms of arthritis.
Understanding Arthritis: Different Types, Effects, and Treatments
Arthritis is not a single disease but a term that encompasses over 100 different types of joint pain and joint diseases. The most common types include osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and gout. Each type has its unique causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
1.Osteoarthritis (OA): This is the most common form of arthritis, resulting from the wear and tear of cartilage—the protective tissue at the ends of bones. It typically affects older adults and commonly impacts the knees, hips, and hands.
2.Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): RA is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the synovium—the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. This causes inflammation, swelling, and eventually leads to joint deformity.
3.Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA): This type of arthritis affects some people with psoriasis—a condition characterized by red patches of skin topped with silvery scales. PsA causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
4.Gout: Gout is characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and tenderness in joints, often the joint at the base of the big toe. It is caused by an excess of uric acid in the blood, leading to the formation of urate crystals in the joints.
Traditional Treatments for Arthritis
Traditional treatments for arthritis aim to reduce symptoms and improve joint function. These treatments include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologics.
- Physical Therapy: Exercise and physical therapy can strengthen muscles around the joints, improve range of motion, and reduce pain.
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss, a healthy diet, and stress management can help manage symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement or repair surgery may be necessary.
While these treatments can be effective, they often come with side effects and may not be suitable for everyone. This has led to growing interest in alternative treatments like CBD.
Speaking of CBD…
CBD, short for cannabidiol, is one of over 100 chemical compounds known as cannabinoids found in the Cannabis sativa plant. Unlike its more famous cousin THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), CBD is non-psychoactive, meaning it does not produce the "high" associated with cannabis use. Cannabidiol is typically extracted from hemp—a variety of cannabis with low THC levels—and is available in various forms, including oils, tinctures, capsules, edibles, and topical creams.
How CBD Works
CBD interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex cell-signaling system that plays a role in regulating a wide range of functions and processes, including pain, inflammation, mood, and immune response. The ECS comprises three main components:
1.Endocannabinoids: These are naturally occurring cannabinoids produced by the body.
2.Receptors: These are found throughout the body and include CB1 receptors (primarily in the central nervous system) and CB2 receptors (primarily in the peripheral nervous system and immune cells).
3.Enzymes: These break down endocannabinoids once they have carried out their function.
CBD is thought to influence the ECS by preventing the breakdown of endocannabinoids, enhancing their effects, and interacting with other receptors in the body, such as serotonin and vanilloid receptors, which are involved in pain and inflammation.
Potential Benefits of CBD for Arthritis
Several potential benefits of CBD for arthritis have been identified, including the following:
1.Pain Relief: CBD has been shown to have analgesic (pain-relieving) properties. By interacting with receptors in the ECS and other pain-related systems, CBD may help reduce the perception of pain in arthritis patients.
2.Anti-inflammatory Effects: Inflammation is a key factor in arthritis. CBD’s interaction with the CB2 receptors, which are involved in immune response, may help reduce inflammation and, consequently, alleviate pain and swelling in affected joints.
3.Improved Sleep: Chronic pain from arthritis can interfere with sleep, leading to fatigue and reduced quality of life. CBD’s calming effects on the nervous system can help promote better sleep, which is crucial for overall health and well-being.
4.Reduced Anxiety and Depression: Chronic pain and reduced mobility can lead to anxiety and depression in arthritis patients. CBD’s potential to influence serotonin receptors may help alleviate these symptoms, improving the overall mental health of individuals with arthritis.
Research on CBD and Arthritis
Research on CBD for arthritis is still in its early stages, but several studies and anecdotal evidence suggest promising results:
1.Preclinical Studies: Animal studies have shown that CBD can reduce inflammation and pain in models of arthritis. For example, a 2016 study published in the European Journal of Pain found that topical CBD application had the potential to relieve pain and inflammation associated with arthritis in rats without evident side effects.
2.Human Studies: Human studies are more limited, but some clinical trials and surveys have indicated positive outcomes. A 2018 study published in the Journal of Pain Research found that CBD was effective in reducing pain and improving sleep in patients with chronic pain conditions, including arthritis.
3.Anecdotal Evidence: Many arthritis patients report relief from symptoms after using CBD products. This anecdotal evidence has led to increased interest and further research into CBD as a potential treatment for arthritis.
How to Use CBD for Arthritis
If you’re considering using CBD for arthritis, it is important to consult with your doctor/physician, as they can help determine the appropriate dosage and form. With that being said, here are some general guidelines:
1.Forms of CBD: CBD is available in various forms, including vapes, tinctures, capsules, edibles, and topical creams. Topical CBD products may be particularly beneficial for arthritis as they can be applied directly to the affected joints.
2.Dosage: There is no one-size-fits-all dosage for CBD. It is recommended to start with a low dose and gradually increase until you achieve the desired effects. Your healthcare provider can help you determine the right dosage based on your specific needs and condition.
3.Quality: Choose high-quality CBD products from reputable manufacturers. Look for products that have been third-party tested for purity and potency.
4.Potential Side Effects: CBD is generally well-tolerated, but some people may experience side effects such as dry mouth, diarrhea, reduced appetite, drowsiness, and fatigue. It is important to monitor your body’s response and adjust the dosage as needed.
Future Directions and Research
While the current evidence is promising, more rigorous clinical trials are needed to fully understand the efficacy and safety of CBD for arthritis. Future research should focus on:
- §Long-term Effects: Studying the long-term effects of CBD use in arthritis patients to ensure safety and efficacy.
- §Dosage Guidelines: Establishing standardized dosing guidelines to help patients achieve optimal benefits.
- §Mechanisms of Action: Further elucidating the mechanisms through which CBD interacts with the ECS and other pathways involved in arthritis.
- §Combination Therapies: Investigating the potential benefits of combining CBD with other treatments, such as traditional medications or physical therapy.
Overall, cannabidiol holds significant promise as a potential treatment for various forms of arthritis. It’s different properties make it an attractive option for those seeking alternative or complementary therapies.
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...